Sep 28, 2023The two strands are complementary rather than identical and are held together by hydrogen bonds between specific pairs of bases, A with T and C with G. That is, whenever an A base occurs in one strand, a T base occurs opposite it in the other strand; when a C base occurs in one, a G occurs in the other (Figure 28.3).
Complementary Base Pairs in DNA and RNA – YouTube
DNA complementary base pairing Credit: Madeleine Price Ball Remember that nucleotides of the DNA have the property of base pairing, where the letter A (Adenine) forms a hydrogen bond with the letter T (Thymine) and the letter C (Cytocine) forms a hydrogen bond with the letter G (Guanine). Let’s use an example of a string of DNA like this:

Source Image: igcse-biology-2017.blogspot.com
Download Image
DNA is well-suited to perform this biological function because of its molecular structure, and because of the development of a series of high performance enzymes that are fine-tuned to interact with this molecular structure in specific ways.
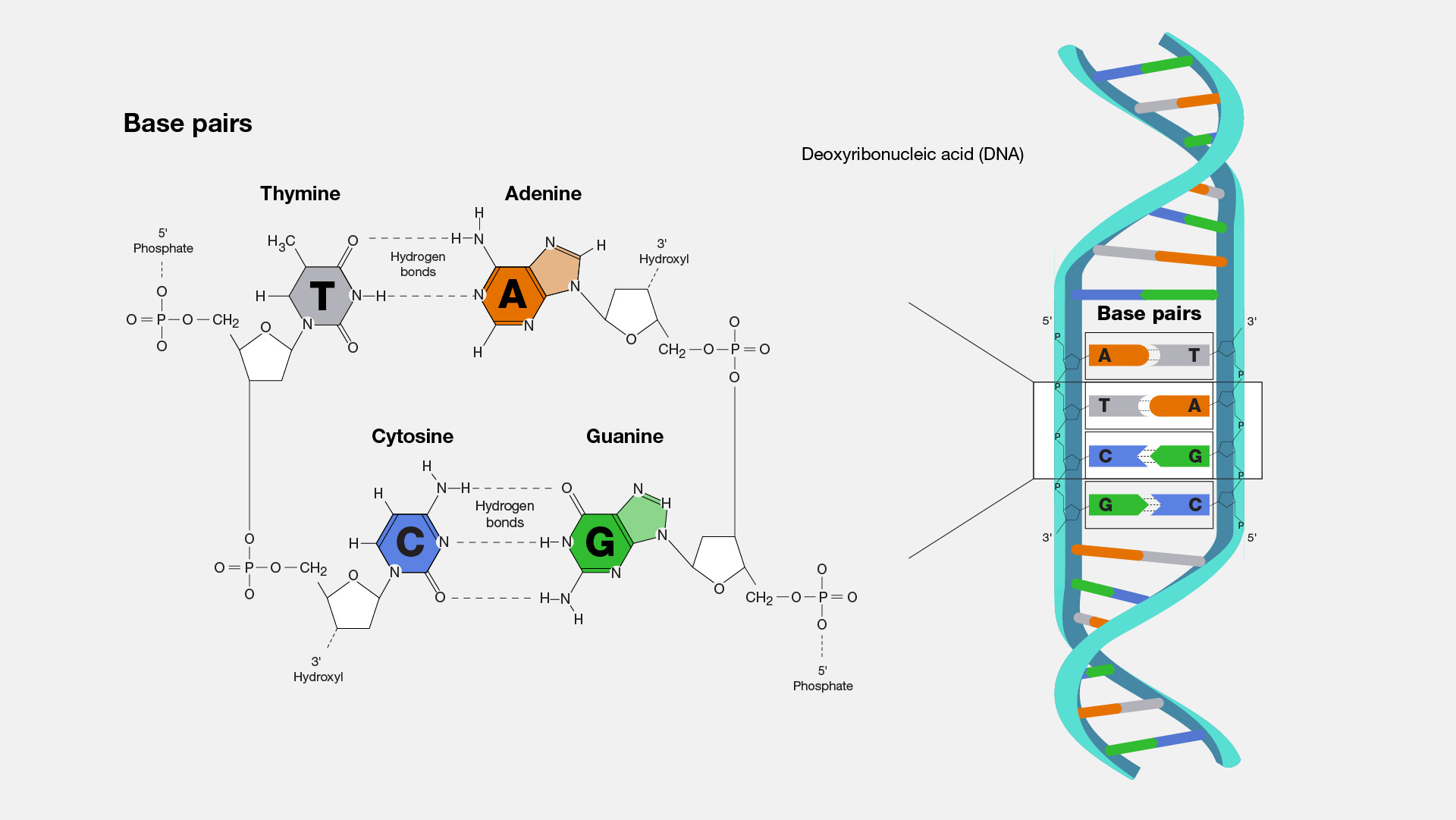
Source Image: genome.gov
Download Image
Question Video: Identifying Complementary Bases in DNA | Nagwa Figure 2. Two strains of S. pneumoniae were used in Griffith’s transformation experiments. The R strain is non-pathogenic. The S strain is pathogenic and causes death. When Griffith injected a mouse with the heat-killed S strain and a live R strain, the mouse died. The S strain was recovered from the dead mouse.

Source Image: studypool.com
Download Image
Which Shows The Correct Complementary Base Pairing For Dna
Figure 2. Two strains of S. pneumoniae were used in Griffith’s transformation experiments. The R strain is non-pathogenic. The S strain is pathogenic and causes death. When Griffith injected a mouse with the heat-killed S strain and a live R strain, the mouse died. The S strain was recovered from the dead mouse. Test Pages DNA structure Base pairing Organisation of DNA Base pairing The nucleotides are identical except for the base, which can be an adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine. There are
SOLUTION: Ib biology chapter 2.7 replication transcription and translation – Studypool
A complementary strand of DNA or RNA may be constructed based on nucleobase complementarity. Each base pair, A = T vs. G ≡ C, takes up roughly the same space, thereby enabling a twisted DNA double helix formation without any spatial distortions. Hydrogen bonding between the nucleobases also stabilizes the DNA double helix. Complementary Base Pairs in DNA and RNA – YouTube

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Complementary Base Pairs – YouTube A complementary strand of DNA or RNA may be constructed based on nucleobase complementarity. Each base pair, A = T vs. G ≡ C, takes up roughly the same space, thereby enabling a twisted DNA double helix formation without any spatial distortions. Hydrogen bonding between the nucleobases also stabilizes the DNA double helix.

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Complementary Base Pairs in DNA and RNA – YouTube Sep 28, 2023The two strands are complementary rather than identical and are held together by hydrogen bonds between specific pairs of bases, A with T and C with G. That is, whenever an A base occurs in one strand, a T base occurs opposite it in the other strand; when a C base occurs in one, a G occurs in the other (Figure 28.3).

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Question Video: Identifying Complementary Bases in DNA | Nagwa DNA is well-suited to perform this biological function because of its molecular structure, and because of the development of a series of high performance enzymes that are fine-tuned to interact with this molecular structure in specific ways.

Source Image: nagwa.com
Download Image
FREE) 2.9 (i), (ii) – Structure of DNA & Complimentary Base Pairings – IAL Biology – Edexcel | Teaching Resources Explain why complementary base pairing is necessary to maintain the double helix shape of the DNA molecule. This page titled 4.3: DNA Structure and Replication is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a

Source Image: tes.com
Download Image
Base Pair | Talking Glossary of Genetic Terms | NHGRI | Biology classroom, Biochemistry, Genetics Figure 2. Two strains of S. pneumoniae were used in Griffith’s transformation experiments. The R strain is non-pathogenic. The S strain is pathogenic and causes death. When Griffith injected a mouse with the heat-killed S strain and a live R strain, the mouse died. The S strain was recovered from the dead mouse.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Test: DNA Structure And Function! Quiz – Trivia & Questions Test Pages DNA structure Base pairing Organisation of DNA Base pairing The nucleotides are identical except for the base, which can be an adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine. There are
(183).jpg)
Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
Complementary Base Pairs – YouTube
Test: DNA Structure And Function! Quiz – Trivia & Questions DNA complementary base pairing Credit: Madeleine Price Ball Remember that nucleotides of the DNA have the property of base pairing, where the letter A (Adenine) forms a hydrogen bond with the letter T (Thymine) and the letter C (Cytocine) forms a hydrogen bond with the letter G (Guanine). Let’s use an example of a string of DNA like this:
Question Video: Identifying Complementary Bases in DNA | Nagwa Base Pair | Talking Glossary of Genetic Terms | NHGRI | Biology classroom, Biochemistry, Genetics Explain why complementary base pairing is necessary to maintain the double helix shape of the DNA molecule. This page titled 4.3: DNA Structure and Replication is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a