A Collection by Ashley Steele Share Similar ideas popular now Organic Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry Physical Science Science Classroom Homeschool High School Teaching High School School Help Homeschool Science Student Teaching Science Education School Work Chemistry Help Teaching Chemistry H Homework Help at Classof1 Organic chemistry
Competing Reactions of Vinyl and Hydroxyl Groups of Vinyl Alcohol on Ge(100): Effects of Vinyl Substituent on Dissociative Adsorption | The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
Dec 14, 2023Vinyl compounds contain the hydrocarbon vinyl group (CH 2 =CH-). The molecules of a single vinyl compound can be made to polymerize; that is, to join end to end, forming a polyvinyl compound such as polyvinyl chloride. The molecules of two different compounds can also be made to link up, forming a copolymer, such as the plastic Vinylite and the

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Now that we have a basic understanding of what allyl and vinyl mean, let’s explore their properties and uses in more detail. Allyl. Allyl is a functional group in organic chemistry that contains a carbon-carbon double bond and a methylene group attached to the double bond. The allyl group is commonly represented as -CH2CH=CH2.

Source Image: juppsfloorcoverings.com.au
Download Image
Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Vinyl halide. General structure of a vinyl halide, where X is a halogen and R is a variable group. In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula CH 2 =CHX (X = halide ). The term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason, alkenyl halides with the formula RCH=CHX are sometimes called vinyl halides.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
What Does Vinyl Mean In Organic Chemistry
Vinyl halide. General structure of a vinyl halide, where X is a halogen and R is a variable group. In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula CH 2 =CHX (X = halide ). The term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason, alkenyl halides with the formula RCH=CHX are sometimes called vinyl halides. Jan 23, 2023The rigorous IUPAC system for naming alkene isomers, called the E-Z system, is based on the same priority rules.These priority rules are often called the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) rules, after the chemists who developed the system. The general strategy of the E-Z system is to analyze the two groups at each end of the double bond.
430 Best Organic Chemistry ideas | organic chemistry, chemistry, organic chem
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry – Vinyl group Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Vinyl group : A portion of a molecular structure equivalent to ethylene ( ethene ) minus one hydrogen atom. Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Nomenclature Examples Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry – Vinyl group Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Vinyl group : A portion of a molecular structure equivalent to ethylene ( ethene ) minus one hydrogen atom.
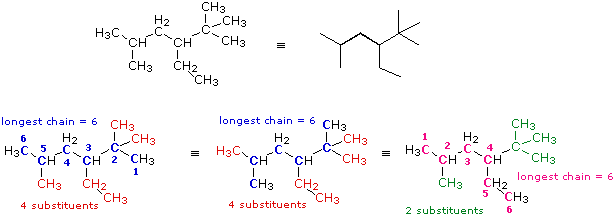
Source Image: www2.chemistry.msu.edu
Download Image
Competing Reactions of Vinyl and Hydroxyl Groups of Vinyl Alcohol on Ge(100): Effects of Vinyl Substituent on Dissociative Adsorption | The Journal of Physical Chemistry C A Collection by Ashley Steele Share Similar ideas popular now Organic Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry Physical Science Science Classroom Homeschool High School Teaching High School School Help Homeschool Science Student Teaching Science Education School Work Chemistry Help Teaching Chemistry H Homework Help at Classof1 Organic chemistry

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Now that we have a basic understanding of what allyl and vinyl mean, let’s explore their properties and uses in more detail. Allyl. Allyl is a functional group in organic chemistry that contains a carbon-carbon double bond and a methylene group attached to the double bond. The allyl group is commonly represented as -CH2CH=CH2.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics 14 Share 508 views 1 year ago Fundamental concepts_Organic Chemistry Most of the time students are confused with the allyl, vinyl, benzyl and aryl groups. They also struggle to identify those

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
What are VOCs and How Do You Remove Them? – Fresh Water Systems Vinyl halide. General structure of a vinyl halide, where X is a halogen and R is a variable group. In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula CH 2 =CHX (X = halide ). The term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason, alkenyl halides with the formula RCH=CHX are sometimes called vinyl halides.

Source Image: freshwatersystems.com
Download Image
Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Jan 23, 2023The rigorous IUPAC system for naming alkene isomers, called the E-Z system, is based on the same priority rules.These priority rules are often called the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) rules, after the chemists who developed the system. The general strategy of the E-Z system is to analyze the two groups at each end of the double bond.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Nomenclature Examples
Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Dec 14, 2023Vinyl compounds contain the hydrocarbon vinyl group (CH 2 =CH-). The molecules of a single vinyl compound can be made to polymerize; that is, to join end to end, forming a polyvinyl compound such as polyvinyl chloride. The molecules of two different compounds can also be made to link up, forming a copolymer, such as the plastic Vinylite and the
Vinyl Derivative – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics What are VOCs and How Do You Remove Them? – Fresh Water Systems 14 Share 508 views 1 year ago Fundamental concepts_Organic Chemistry Most of the time students are confused with the allyl, vinyl, benzyl and aryl groups. They also struggle to identify those