These data together suggest that the pathogenesis of Type 1 diabetes affects the hypothalamic pituitary axis resulting in decreased LH secretion. The low LH response may have negative implications on steroidogenesis from the Leydig cells, resulting in impaired spermatogenesis.
Diabetes Education Stock Illustrations – 760 Diabetes Education Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime
In persons with type 1 diabetes, however, control of glucose homeostasis during exercise is extremely challenging, as insulin levels cannot change rapidly in response to exercise, and there may be deficiencies or exaggerations in other hormonal responses. 8 As a result of a variety of unpredictable factors, exercise may cause either

Source Image: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Download Image
January 24, 2022 An estimated 30 million Americans have diabetes, a disease in which there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. About 7 million of them, however, have not yet been diagnosed with the disease. Endocrine Connection

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Three weeks of time-restricted eating improves glucose homeostasis in adults with type 2 diabetes but does not improve insulin sensitivity: a randomised crossover trial – published online 25/07/2022 – Diabetologia Glucose homeostasis is dependent on hormonal control, most notably through the actions of insulin and glucagon but also adrenalin, cortisol, and estrogens, and there is increasing evidence that EDCs may be contributing to causation of the glucose imbalances in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (see Chapter 16 ).
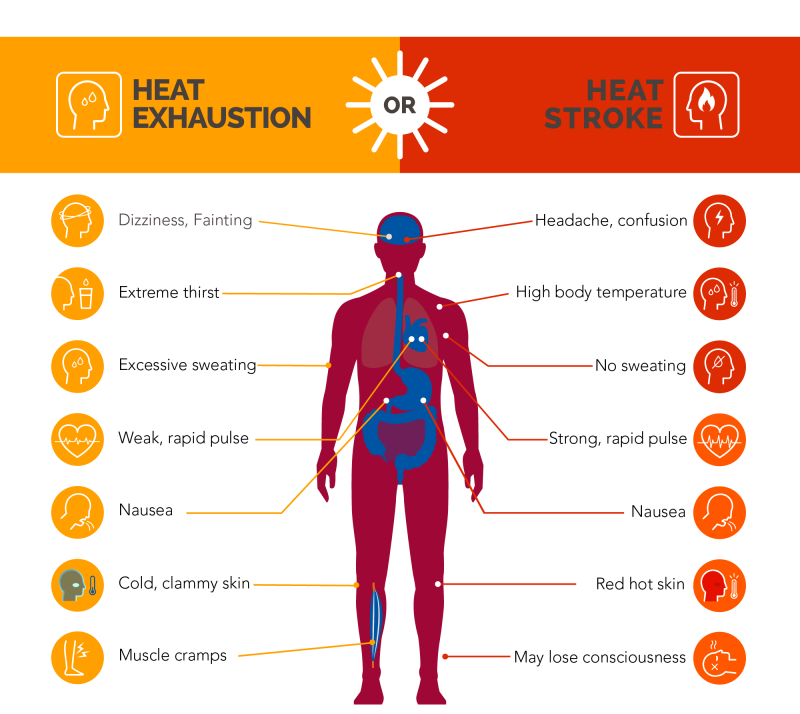
Source Image: letstalkscience.ca
Download Image
How Does Type 1 Diabetes Affect Homeostasis
Glucose homeostasis is dependent on hormonal control, most notably through the actions of insulin and glucagon but also adrenalin, cortisol, and estrogens, and there is increasing evidence that EDCs may be contributing to causation of the glucose imbalances in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (see Chapter 16 ). Introduction Glucose plays an important role in metabolism. It is not only the source of energy, but also the substrate of cell composition biosynthesis ( 1 ). The metabolic dysregulation of glucose homeostasis is the main consequence of the development of diabetes and the major cause of diabetic morbidity and mortality.
Introduction to Homeostasis and Regulation | Let’s Talk Science
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition. In this condition, the pancreas makes little or no insulin. … Over time, type 1 diabetes complications can affect major organs in the body. These organs include the heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. Having a normal blood sugar Type 1 Diabetes and Dysfunctional Intestinal Homeostasis: Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism

Source Image: cell.com
Download Image
Managing Blood Sugars When You Have Type 1 Diabetes (for Teens) – Nemours KidsHealth Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition. In this condition, the pancreas makes little or no insulin. … Over time, type 1 diabetes complications can affect major organs in the body. These organs include the heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. Having a normal blood sugar
Source Image: kidshealth.org
Download Image
Diabetes Education Stock Illustrations – 760 Diabetes Education Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime These data together suggest that the pathogenesis of Type 1 diabetes affects the hypothalamic pituitary axis resulting in decreased LH secretion. The low LH response may have negative implications on steroidogenesis from the Leydig cells, resulting in impaired spermatogenesis.

Source Image: dreamstime.com
Download Image
Three weeks of time-restricted eating improves glucose homeostasis in adults with type 2 diabetes but does not improve insulin sensitivity: a randomised crossover trial – published online 25/07/2022 – Diabetologia January 24, 2022 An estimated 30 million Americans have diabetes, a disease in which there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. About 7 million of them, however, have not yet been diagnosed with the disease. Endocrine Connection
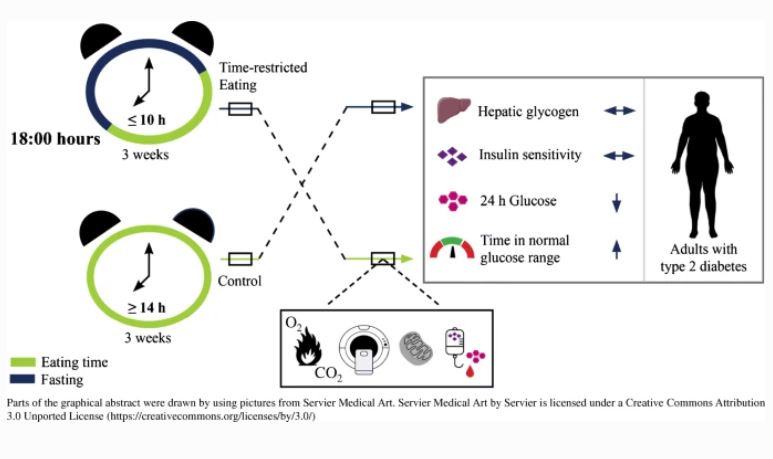
Source Image: diabetologia-journal.org
Download Image
Malfunctions | VCE BioNinja increased thirst and urination increased hunger blurred vision fatigue
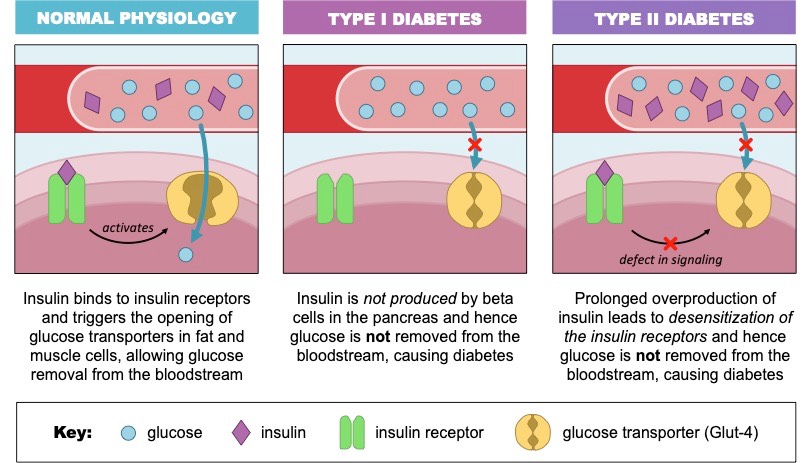
Source Image: vce.bioninja.com.au
Download Image
Homeostasis: positive/ negative feedback mechanisms | Basic anatomy and physiology, Physiology, Human anatomy and physiology Glucose homeostasis is dependent on hormonal control, most notably through the actions of insulin and glucagon but also adrenalin, cortisol, and estrogens, and there is increasing evidence that EDCs may be contributing to causation of the glucose imbalances in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (see Chapter 16 ).

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Introduction to Homeostasis and Regulation | Let’s Talk Science Introduction Glucose plays an important role in metabolism. It is not only the source of energy, but also the substrate of cell composition biosynthesis ( 1 ). The metabolic dysregulation of glucose homeostasis is the main consequence of the development of diabetes and the major cause of diabetic morbidity and mortality.
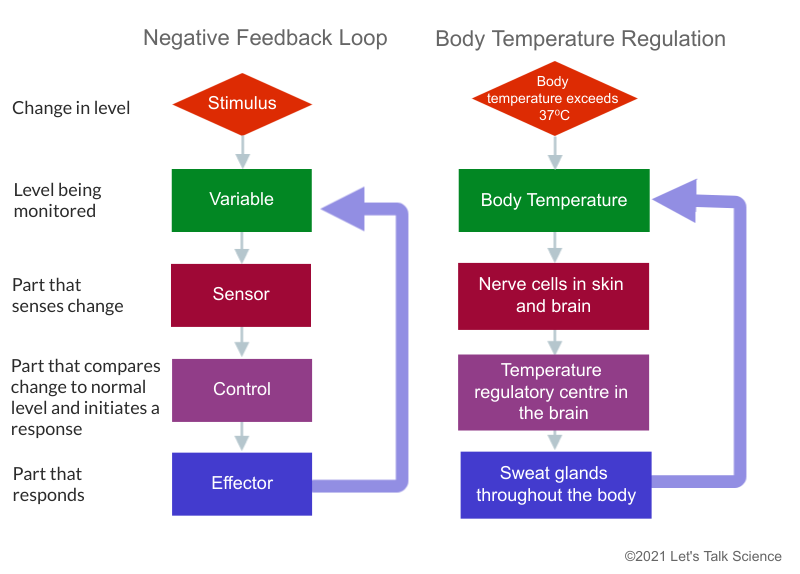
Source Image: letstalkscience.ca
Download Image
Managing Blood Sugars When You Have Type 1 Diabetes (for Teens) – Nemours KidsHealth
Introduction to Homeostasis and Regulation | Let’s Talk Science In persons with type 1 diabetes, however, control of glucose homeostasis during exercise is extremely challenging, as insulin levels cannot change rapidly in response to exercise, and there may be deficiencies or exaggerations in other hormonal responses. 8 As a result of a variety of unpredictable factors, exercise may cause either
Three weeks of time-restricted eating improves glucose homeostasis in adults with type 2 diabetes but does not improve insulin sensitivity: a randomised crossover trial – published online 25/07/2022 – Diabetologia Homeostasis: positive/ negative feedback mechanisms | Basic anatomy and physiology, Physiology, Human anatomy and physiology increased thirst and urination increased hunger blurred vision fatigue